How 5-axis machining of automobile engine housings
Release time:
2025-07-31 17:37
The specific process of GD prototyping 5-axis CNC machining of automotive engine housings generally includes the following key steps, which, combined with the machine's multi-axis linkage, enable efficient and precise machining of complex shapes:
1. Workpiece Clamping and Positioning
Workpiece Clamping: The engine housing blank is clamped on the worktable of the 5-axis machining center to ensure stability and facilitate 5-axis linkage.
Positioning and Measurement: The machine's probe or coordinate measuring device is used to determine the workpiece's reference points and coordinate system, ensuring accurate machining paths.
2. Roughing (Extensive Material Removal)
Roughing is performed using 3-axis or partial 5-axis linkage to remove most of the excess material from the blank.
High-speed cutting using a large-diameter milling cutter or end mill ensures efficient material removal.
This step primarily ensures that the workpiece dimensions and shape remain close to the design requirements during subsequent finishing.
3. Semi-finishing (Combined Roughing and Finishing of Complex Areas)
Using 5-axis linkage, the tool angle is adjusted to avoid the fixture and protruding parts of the workpiece.
Semi-finishing of complex areas is performed, approaching the final dimensions but leaving a small amount of stock.
5-axis machine tools adjust tool direction to achieve efficient machining of deep cavities, inclined surfaces, and curved surfaces.
4. Finishing (Surface Quality and Dimensional Accuracy)
Use ball-end cutters and other precision tools for full 5-axis simultaneous finishing.
The tool angle dynamically adjusts as the workpiece surface changes, ensuring the cutting edge always maintains the optimal cutting angle with the workpiece surface.
Production of smooth surfaces and precise geometric shapes, meeting design dimensional tolerances and surface finish requirements.
5. Chamfering and Holemaking
Machining critical mounting holes and threaded holes to ensure positional and dimensional accuracy.
Perform auxiliary machining such as chamfering and trimming to improve assembly performance.
6. Real-time Monitoring During Machining
Utilize the machine's built-in sensors and probes to monitor machining status in real time.
Compensate for tool wear and workpiece deformation to ensure consistent machining quality.
Key Technical Points of 5-Axis Machining
Tool Path Planning: Complex curved surfaces utilize multi-axis simultaneous tool path design to avoid interference and ensure stable cutting.
Tool Selection: Use a combination of ball-end milling cutters, angled milling cutters, and reamers.
Cooling and Lubrication: Make full use of the machine tool nozzles to spray cutting fluid, reducing cutting heat and extending tool life.
Fixture Design: Specially designed fixtures support multi-faceted machining without affecting tool motion.
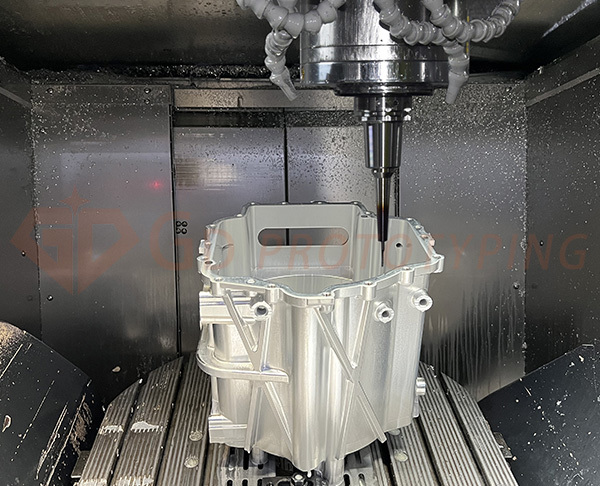
Advantages of 5-Axis CNC Machining for Automotive Engine Housings
1. High-Precision and Complex Shape Machining
5-axis machining can simultaneously control multiple rotation angles of the workpiece and tool, enabling machining of complex curved surfaces and multiple angles, meeting the complex geometry requirements of engine housings.
2. Reduced Clamping Times
Traditional 3-axis machining requires multiple clampings to adjust the workpiece position, increasing errors and time costs. 5-axis machining can complete multi-faceted machining in a single clamping, improving machining accuracy and efficiency.
3. Improved Machining Efficiency
Through appropriate tool path planning, 5-axis machining reduces tool change and angle adjustment time, shortening machining cycles.
4. Extended Tool Life
5-axis machining allows the tool to maintain the optimal cutting angle, reducing cutting forces and vibration, and extending tool life.
5. Improved surface quality
Since cutting can be performed at the optimal angle, the surface is smoother and subsequent finishing steps are reduced.
preceding page
preceding page
Related News
2024-04-05




